Here are 12 essential computing terms that are frequently used by computing students. Get to know them and prepare yourself for an exciting coding journey ahead.
Computing Terms – General
1. Git
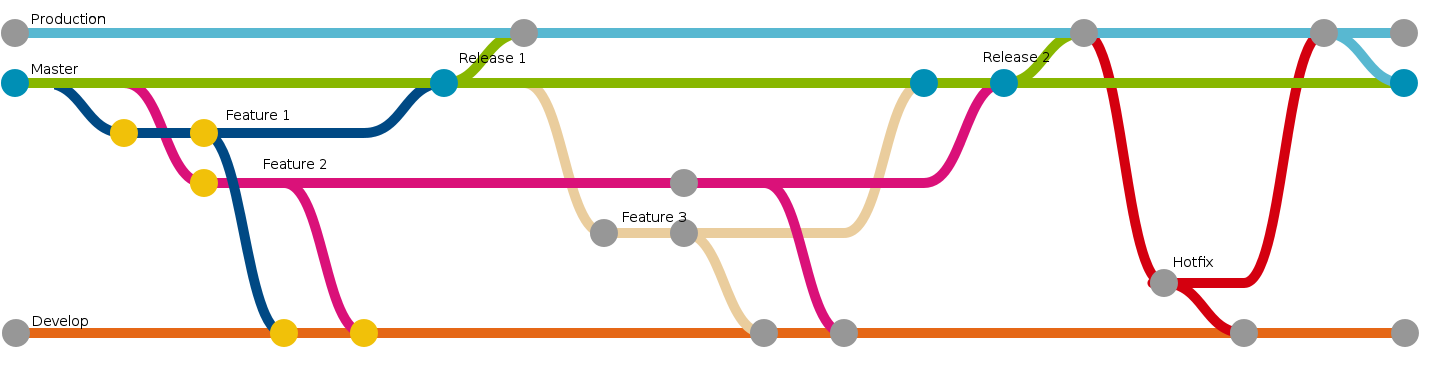
An illustration of Git workflow
Git (acronym for global information tracker, if you like) is a version control software (VCS) that helps you keep track of the code during development and collaborate with others.
Think of git as a Google Drive app for your code:
- Save your progress on coding locally (using “git commit” command in git).
- Push your progress remotely “to the cloud” (using “git push” command in git).
- Retrieve your progress from remote “cloud” (using “git pull” command in git).
- Edit on the same code together with you friends (using “git branch” and “git checkout” commands in git) and combine them later (using “git merge” command in git).
- And many other more powerful things…
Learn git: Just Google git tutorial or pick up a desktop client if you are scared of typing into command line and want a “normal application” where you can use your mouse to click.
Related terms:
- GitHub
GitHub is an online platform where you can store your code with git, think of it as Google Drive or Dropbox…
But wait, I thought git is Google Drive? Yeah, I know. It is a bit confusing, but think of git as a unified app for managing code across different online storage providers. Instead of having both Google Drive and Dropbox app installed on your computer, you only have one single app, which can connect to either Google Drive or Dropbox. Git is that one single app.
GitHub, on the other hand, is just a popular choice for storing your code. If you don’t like Google Drive, then there is Dropbox. Similarly, if you don’t like GitHub, there are alternatives such as Bitbucket.
(If you are not confused at this point, there are also alternatives for git, such as mercurial, but those are not so popular now)
- Pull Request (PR)

Pull Request workflow on BitBucket
This is a term commonly used in software development, especially open-source software. Pull requests are a way to integrate new changes to the source code in a distributed VCS such as Git or Mercurial.
When a contributor implements a new feature, or a bug fix, he will be able to send a pull request (via hosting services such as GitHub or BitBucket) to the core developers. The core developers would be able to review the code and discuss it with the contributor within the pull request. If the changes are accepted, the pull request can be merged into the source code. Finally, the existing developers for the project would need to “pull” the new changes, hence the name pull request.
2. Linux

Linux command line interface
Linux is an operating system, like Windows or OS X (operating system on Mac/Macbook by Apple). The main difference is that Linux is open source, you can see its main (kernel) source code on GitHub. Due to similarities in their origin from UNIX, OS X is often considered a Linux-like OS, so some of the points below are also applicable to OS X.
There are some reasons why Linux is better for programming:
- Typing commands into the terminal instead of clicking mouse. This boosts productivity and allows you to familiarize with some standard shell commands that other programmers use (such as “<” and “>” for piping input and output).
- Allows (forces) you to learn some good-to-know knowledge on operating systems, like file system, processes.
- It is widely used by programmers, so chances are online coding tutorials and guides are written with the assumption that you are on Linux (or OS X).
- Lot of software libraries and packages (especially web development) that are either only available on Linux (or OS X), or extremely troublesome to install and setup on Windows.
In a nutshell, using Linux would save you a lot of trouble when doing programming, OS X is also good in this respect. You may be able to run Linux on Windows in the future, but for now it is better to get a Linux distribution like Ubuntu (see below) on your computer (via dual boot or virtual machine).
Related terms:
- Ubuntu

Screenshot of Ubuntu Desktop
Ubuntu is a Debian-based Linux distribution, i.e. an operating system based on Linux. It gives you more features on top of Linux. It provides a graphical user interface similar to Windows and OS X, and built-in word processing software similar to Microsoft Office.
Normally when people say install Linux, they are referring to installing a Linux distribution such as Ubuntu.
3. Integrated Development Environment (IDE)

A screenshot of IntelliJ IDEA IDE
If you are a techie, then you have probably heard of the debates on IDE vs text editors. IDEs are basically text editors with more features, such as code completion, debugging, building and testing. They can be specific to a language or framework, or more general and support different languages via tons of extensions and plugins. Some of the popular IDEs are IntelliJ IDEA (support many languages), Eclipse (for Java and JavaScript), Visual Studio (for C++ on Windows), XCode (support many languages on OS X, the operating system for Mac).
Chances are you don’t need them until you take the module CS2103 (or CS2103T) Software Engineering, in which you will be using Eclipse (or hopefully something more modern). For introductory modules on algorithms and data structures, you don’t really need an IDE unless you need to do advanced debugging using breakpoints.
However, if you want to try developing a web app or mobile app, then you would want to get an IDE (XCode or iOS app, Android Studio for Android app, IntelliJ IDEA or WebStorm for web app). Using an IDE would allow you to test, build and deploy easier and save you a lot of manual work (unless you are already an avid Vim or Emacs user).
Related terms:
- Vim/Emacs

Screenshot of Vim
These are the two most “respected” text editors within the programming world. They are not IDEs but more powerful than normal text editors. Both of them are designed to minimize mouse usage in order to achieve higher efficiency. They can be customized and extended via plugins. Moreover, they do not rely on GUI of the operating system, making them the only options (besides nano, a very basic text editor) to edit text directly on servers via command line interface. Vim also come with major operating systems used in servers so you can use it right away without installation.
- Sublime Text/Atom
Screenshot of Sublime Text
These are relatively new text editors that the younger generation tend to use. They offer fancy graphical user interface and tons of plugins to save a lot of effort in coding. They have keyboard shortcuts but do not explicitly discourage the use of mouse and clicking. Unlike Vim/Emacs which requires you to spend time learning how to use them, Sublime Text/Atom are more friendly to beginners. If you think Vim/Emacs are too geeky, then get one of these instead.
Computing Terms – Web Development
In general,terms in the area of web development can be divided into two categories, front-end and back-end, I will start with front-end first.
front-end and back-end
4. Front-end (client-side)
Front-end, i.e. the client side of the web development, typically involves developing contents that normal users see in their browser. The core of front-end development is broken into 3 inter-connected components, HTML (HyperText Markup Language), CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) and JavaScript.
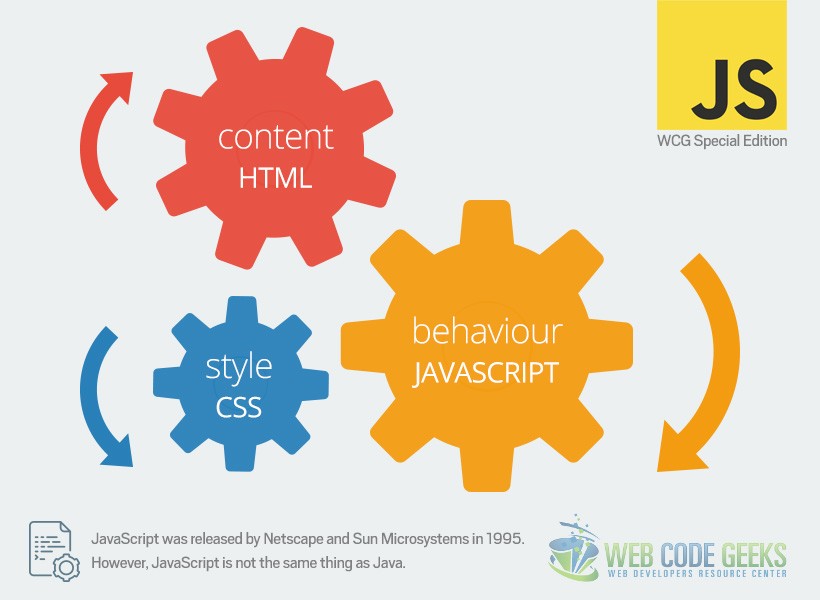
Different roles of HTML, CSS and JavaScript
5. HTML (HyperText Markup Language)
HTML serves as the skeleton of the web pages, it defines the structure and the content of the webpage that appears in the browser. It is the only essential component of a web page, i.e. you cannot write a web page without HTML. But it is also the most simple and basic component of the 3, as it is just a markup language. This means you cannot write logic in HTML like in programming languages such as C++ or Java, HTML only defines how the contents are presented.
A webpage written in HTML typically have many HTML elements of various types (called HTML tags). Another popular markup language is markdown, which is typically used to write documentations and guides for software projects.
6. CSS (Cascading Style Sheets)
CSS is basically used to “decorate” the HTML, if HTML is the human body, then CSS is the clothes. It can be used to style the HTML in almost every way you can possibly imagine: size, position, color, interactivity, animation. Unlike HTML, you can use some limited logic inside CSS, such as differentiating the even and odd number.
Without CSS, web pages will be dry and boring. CSS allows web pages to have nice looks, it is also responsible for some of the dynamic contents and interactions on the web page. However, the most powerful way to build interactions on web pages is to use JavaScript.
7. JavaScript
JavaScript is an implementation of ECMAScript. Below is a screenshot of ECMAScript’s Wikipedia page on the relationship between ECMAScript, JavaScript and the various browsers:
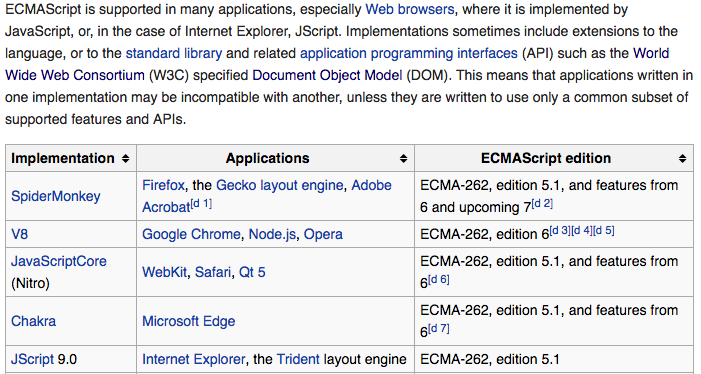
Relationship between JavaScript, ECMAScript and the browsers, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ECMAScript
Unlike HTML and CSS, JavaScript is a full Programming language, just Java or C++, i.e. you can write any kind of logic inside it. But it is very different from Java.
Java and Javascript are similar like Car and Carpet are similar.
JavaScript was designed to be used in web pages to compliment HTML and add interactivity into it. You can use JavaScript codes inside a HTML page to access and modify the HTML elements within the page, via Document Object Model (DOM).
For example, to build a calculator on the web, you would write the structure in HTML, and get user’s input in HTML with the help of JavaScript, calculate the result in JavaScript and finally update the HTML with the result using JavaScript.
Now we can differentiate between web application (web app) and website. Essentially a web app would have some complex JavaScript that resembles an application with a lot of user interactions, on top of HTML and CSS. A website on the other hand would mainly consists of HTML and CSS, without too much JavaScript code.
8. Backend-end (server-side)
What you do not see in the browser, is the backend of the web. The backend is responsible for database operations and “serving” the front-end contents to the user. In a traditional website, when the user requests a webpage, the backend would determine what the user is requesting, get some relevant data from database (optional), generate the corresponding HTML page with CSS and JavaScript, and send them back to the user’s browser.
9. Application Programming Interface (API)

API in the context of web application
This is a very common term used in software engineering, especially when developing web applications. In the context of front-end and back-end, we use a more specific term RESTful API (REST API). It serves as a bridge for front-end to communicate with the backend. APIs are used by the front-end and implemented in the backend, and both sides need to agree on the format of the APIs.
Let’s say the user wants to see his/her list of friends. The front-end would have some functions to call an API (in JavaScript), which sends an HTTP request (see below) to the server (back-end) over the Internet. The server receives the HTTP request in an API endpoint, which then executes some function to retrieve the list of friends from a database. Finally the list is return to the front-end via Internet as a response.
APIs are widely used on many websites and web applications to serve dynamic content for users. An example would be the autocomplete feature on Google: When you type on Google search bar, the browser is actually sending what you are typing as API requests to Google’s server. The server handles the API calls and tries to guess what you want to search, and return the result of top guesses.
Outside the context of front-end and back-end, APIs are a common pattern to allow one component of the system to use functions of another component without explicitly knowing how they are implemented. For example, Android system implemented many APIs to allow Android apps to access functions such as taking pictures, storing data on the phone. App developers just need to use these APIs to obtain the result without worrying what is happening under the hook.
10. HTTP Request
APIs serve as the bridge between front-end and back-end. But in order to implement those APIs, we need the front-end to send HTTP requests and the back-end to reply with responses. Note that the back-end can also communicate with other back-ends by sending HTTP requests.
There are two common HTTP requests, GET and POST.
GET request has an url (which is your server’s location, such as paradite.com) and a query string, the query string serves the same purpose as the parameters of functions. For example, for this simple function:
|
1 2 3 |
function sayHello(name, message) { console.log(name + ': ' + message); } |
In order to use this function, we write something like:
|
1 |
sayHello('Joe', 'Hello'); |
If we write a equivalent GET request that contains the parameters name with value Joe, and message with value Hello, we would have
|
1 |
paradite.com?name=Joe&message=Hello |
Each query parameter has the format of param_name=param_value . Multiple query parameters are joined together with & , the start of query string is indicated by ? .
We need to specify values for query string (parameters) instead of variables in GET request. This is because sending a GET request would be equivalent to calling a function, hence we need values for parameters.
POST request also needs a url. However, in POST request, you need to specify the query string inside the request body. For GET request, you can create it by yourself since it is just a string. But for POST request (and more sophisticated GET request), typically you would have some helper functions to construct POST requests. In front-end, you can use jQuery library to issue POST requests. In back-end, most server-side programming languages and frameworks have some ways (file_get_contents in PHP) to issue POST requests.
Initially, POST is designed to send data to server, where GET is for retrieving data. But in practice, you can use them interchangeably. So why use POST request at all? The POST request has no limit on the length of query string and it is more secure.
11. Error 404
This is just one of the many HTTP status codes. It means the page that you are requesting cannot be found. HTTP status codes are sent from server to your browser to tell the browser what happened. If you are serious about web development and building your own server, then you need to know at least a few other status codes, such as 200, 301, 304, 401, 500, etc…
Computing Terms – Computer Science
12. Recursion
The explanation of recursion is in the word recursion itself. If you are able to understand the previous sentence, then you have grasp the idea of recursion. In computing world, it usually means a function calling itself during the execution repeatedly, until the function hits a base case. But recursion is more of a concept than a technical term, so you can understand it from a non-computing perspective as well. Think of Russian dolls:
russian dolls – recursion
When you open a Russian doll, you will see another Russian doll inside. Then you open that Russian doll again. The process goes on repeatedly until you hit a base case, i.e. the smallest doll.
Another good explanation of recursion found on Quora: https://www.quora.com/How-should-I-explain-recursion-to-a-4-year-old/answer/Aaron-Krolik
Also try searching for recursion in Google and note the Google’s intelligent spelling correction.
Other terms in Computer Science
There are many other terms in Computer Science, depending on your field of study:
- Algorithm and data structure: pointer, DFS, BFS, heap, stack, queue, complexity class, P, NP…
- Operating system: Process, thread, mutex, semaphore, deadlock…
- Artificial Intelligence: Machine learning, simulated annealing, semantic network…
- Computer Network: TCP, UDP, TCP/IP, SSL, DNS, race condition…
- …
- Monad, endofunctor, monoid…
Unlike the terms that I listed here, those terms are specific to a field of study and covered very systematically in different modules of CS degree, so there are really no need for me to cover them and I will leave the job to the lecturers and tutors.
Now that you have learnt the essential terms for your computing degree in layman’s term, feel free to delve into deep into the terms that you are interested in. Chances are, you will need those knowledge at some point in time.
And if you are in the mood to comment, do let me know if you feel that some important terms are missing or if you spot any errors.
Joining NUS School of Computing? Check out my module reviews for various SoC modules:
You might also like these posts that I wrote:

Well written!